Traditional
Sequence |
Integrated Sequence |
Performance Expectation |
| Algebra 1 |
Math 1 |
Math 2 |
Math 3 |
|
| A2.1.A |
|
|
M2.1.A |
A2.1.A |
M3.1.A |
A2.1.A |
Select and justify functions and equations to model and
solve problems . |
| A2.1.B |
|
|
M2.1.B |
A2.1.B |
M3.1.B |
A2.1.B |
Solve problems that can be represented by systems of
equations and inequalities. |
| A2.1.C |
|
|
M2.1.C |
A2.1.C |
M3.1.C |
A2.1.C |
Solve problems that can be represented by quadratic
functions, equations, and inequalities. |
| A2.1.D |
|
|
|
|
M3.1.D |
A2.1.D |
Solve problems that can be represented by exponential
and
logarithmic functions and equations. |
| A2.1.E |
|
|
|
|
M3.1.E |
A2.1.E |
Solve problems that can be represented by inverse
variations of the forms
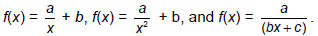 |
| A2.1.F |
|
|
M2.1.E |
A2.1.F |
|
|
Solve problems involving combinations and permutations . |
| A2.2.A |
|
|
|
|
M3.6.A |
A2.2.A |
Explain how whole, integer, rational, real, and complex
numbers are related, and identify the number system(s) within which a
given algebraic equation can be solved. |
| A2.2.B |
|
|
|
|
M3.6.B |
A2.2.B |
Use the laws of exponents to simplify and evaluate
numeric and algebraic expressions that contain rational exponents. |
| A2.2.C |
|
|
|
|
M3.6.D |
A2.2.C |
Add, subtract, multiply , divide, and simplify rational
and more general algebraic expressions. |
| A2.3.A |
|
|
M2.2.C |
A2.3.A |
|
|
Translate between the standard form of a quadratic
function, the vertex form, and the factored form; graph and interpret
the meaning of each form. |
| A2.3.B |
|
|
M2.2.E |
A2.3.B |
|
|
Determine the number and nature of the roots
of a quadratic
function. |
| A2.3.C |
|
|
M2.2.G |
A2.3.C |
|
|
Solve quadratic equations and inequalities, including
equations with complex roots. |
| A2.4.A |
|
|
|
|
M3.3.A |
A2.4.A |
Know and use basic properties of exponential and
logarithmic
functions and the inverse relationship between them. |
| A2.4.B |
|
|
|
|
M3.3.B |
A2.4.B |
Graph an exponential function of the form f(x) = abx and
its inverse logarithmic function. |
| A2.4.C |
|
|
|
|
M3.3.C |
A2.4.C |
Solve exponential and logarithmic
equations. |
| A2.5.A |
|
|
|
|
M3.2.E |
A2.5.A |
Construct new functions using the
transformations
f(x–h), f(x) + k, cf(x), and by adding and subtracting functions , and
describe the effect on the original graph(s). |
| A2.5.B |
|
|
|
|
M3.3.D |
A2.5.B |
Plot points , sketch, and describe the
graphs of functions of the form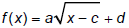 and
solve related equations. and
solve related equations. |
| A2.5.C |
M1.2.D |
A2.5.C |
|
|
M3.3.E |
A2.5.C |
Plot points, sketch, and describe the
graphs of functions of the form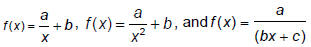 and
solve related and
solve related
equations. |
| A2.5.D |
|
|
|
|
M3.3.F |
A2.5.D |
Plot points, sketch, and describe the
graphs of cubic polynomial functions of the form f(x) = ax^3 + d as an
example of higher order polynomials and solve related equations. |
| A2.6.A |
|
|
M2.4.A |
A2.6.A |
|
|
Apply the fundamental counting
principle and the ideas of order and replacement to calculate
probabilities in situations arising from two -stage experiments (compound
events). |
| A2.6.B |
|
|
M2.4.B |
A2.6.B |
|
|
Given a finite sample space
consisting of equally likely outcomes and containing events A and B,
determine whether A and B are independent or dependent, and find the
conditional probability of A given B. |
| A2.6.C |
|
|
M2.4.C |
A2.6.C |
|
|
Compute permutations and
combinations, and use the results to calculate probabilities. |
| A2.6.D |
|
|
M2.4.D |
A2.6.D |
|
|
Apply the binomial theorem to solve
problems involving probability. |
| A2.6.E |
|
|
M2.2.H |
A2.6.E |
|
|
Determine if a bivariate data set can
be better modeled with an exponential or a quadratic function and use
the model to make predictions |
| A2.6.F |
|
|
|
|
M3.4.A |
A2.6.F |
Calculate and interpret measures of
variability and standard
deviation and use these measures and the characteristics of the normal
distribution to describe and compare data sets. |
| A2.6.G |
|
|
|
|
M3.4.B |
A2.6.G |
Calculate and interpret margin of
error and confidence intervals for population proportions . |
| A2.7.A |
|
|
|
|
M3.3.G |
A2.7.A |
Solve systems of three equations with
three variables. |
| A2.7.B |
|
|
M2.5.D |
A2.7.B |
|
|
Find the terms and partial sums of
arithmetic and geometric series and the infinite sum for geometric
series. |
| A2.8.A |
|
|
|
|
M3.8.A |
A2.8.A |
Analyze a problem situation and
represent it mathematically. |
| A2.8.B |
|
|
|
|
M3.8.B |
A2.8.B |
Select and apply strategies to solve
problems. |
| A2.8.C |
|
|
|
|
M3.8.C |
A2.8.C |
Evaluate a solution for
reasonableness , verify its accuracy, and interpret the solution in the
context of the original problem. |
| A2.8.D |
|
|
|
|
M3.8.D |
A2.8.D |
Generalize a solution strategy for a
single problem to a class of related problems and apply a strategy for a
class of related problems to solve specific problems. |
| A2.8.E |
|
|
|
|
M3.8.E |
A2.8.E |
Read and interpret diagrams, graphs,
and text containing the
symbols, language, and conventions of mathematics. |
| A2.8.F |
|
|
|
|
M3.8.F |
A2.8.F |
Summarize mathematical ideas with
precision and efficiency for a given audience and purpose. |
| A2.8.G |
|
|
|
|
M3.8.G |
A2.8.G |
Use inductive reasoning and the
properties of numbers to make conjectures, and use deductive reasoning
to prove or disprove conjectures. |
| A2.8.H |
|
|
|
|
M3.8.H |
A2.8.H |
Synthesize information to draw
conclusions and evaluate the
arguments and conclusions of others. |