The California Mathematics Content Standards
This discipline complements and expands the mathematical
content and concepts of
Algebra I and geometry. Students who master Algebra II will gain experience with
algebraic
solutions of problems in various content areas, including the solution of
systems of quadratic
equations, logarithmic and exponential functions, the binomial theorem , and the
complex number system.
| |
1.0 Students solve equations and inequalities
involving absolute value. |
Note: The sample
problems illustrate
the standards and
are written to help
clarify them. Some
problems are written
in a form that can be
used directly with
students; others will
need to be modified
before they are
used with students. |
| |
2.0 Students solve systems of linear equations and inequalities (in two
or three
variables) by substitution, with graphs, or with matrices.
Draw the region in the plane that is the solution set for the
inequality
(x - 1)(x + 2y) > 0.
|
|
| |
3.0 Students are adept at operations on polynomials, including long
division.
Divide x4- 3x2 + 3x by x2+ 2.
Write the answer in the form:
 . .
|
|
| |
4.0 Students factor polynomials representing the difference of squares,
perfect
square trinomials, and the sum and difference of two cubes.
|
|
| |
5.0 Students demonstrate knowledge of how real and complex numbers are
related
both arithmetically and graphically. In particular, they can plot
complex
numbers as points in the plane.
|
|
| |
6.0 Students add, subtract , multiply, and divide complex numbers.
|
|
| |
7.0 Students add, subtract, multiply, divide, reduce, and evaluate
rational
expressions with monomial and polynomial denominators and simplify
complicated rational expressions , including those with negative
exponents
in the denominator.7.0 Simplify
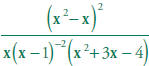
|
|
| |
8.0 Students solve and graph quadratic equations by factoring,
completing the
square, or using the quadratic formula. Students apply these techniques
in
solving word problems. They also solve quadratic equations in the
complex
number system.
In the figure shown below, the area between the two squares is 11
square
inches. The sum of the perimeters of the two squares is 44 inches. Find
the
length of a side of the larger square. (ICAS 1997)
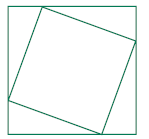
|
|
| |
9.0 Students demonstrate and explain the effect that changing a
coefficient has on
the graph of quadratic functions; that is, students can determine how
the graph
of a parabola changes as a, b, and c vary in the equation y = a(x-b)2+
c.
|
|
| |
10.0 Students graph quadratic functions and determine the maxima,
minima, and
zeros of the function.
Find a quadratic function of x that has zeros at x = -1 and x = 2.
Find a cubic
equation of x that has zeros at x = -1 and x = 2 and nowhere else. (ICAS
1997)
|
|
| |
11.0 Students prove simple laws of logarithms.
11.1 Students understand the inverse relationship between exponents and
logarithms and use this relationship to solve problems involving
logarithms and exponents.
11.2 Students judge the validity of an argument according to whether the
properties of real numbers, exponents, and logarithms have been
applied correctly at each step.
|
|
| |
12.0 Students know the laws of fractional exponents, understand
exponential
functions, and use these functions in problems involving exponential
growth
and decay.
The number of bacteria in a colony was growing exponentially. At 1
p.m.
yesterday the number of bacteria was 100, and at 3 p.m. yesterday it was
4,000.
How many bacteria were there in the colony at 6 p.m. yesterday? (TIMSS)
|
|
| |
13.0 Students use the definition of logarithms to translate between
logarithms in
any base.
|
|
| |
14.0 Students understand and use the properties of logarithms to
simplify logarithmic
numeric expressions and to identify their approximate values.
Find the largest integer that is less than:
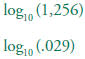
|
|
| |
15.0 Students determine whether a specific algebraic statement involving
rational
expressions, radical expressions , or logarithmic or exponential
functions is
sometimes true, always true, or never true.
|
|
| |
16.0 Students demonstrate and explain how the geometry of the graph of a
conic
section (e.g., asymptotes, foci, eccentricity) depends on the
coefficients of the
quadratic equation representing it.
|
|
| |
17.0 Given a quadratic equation of the form ax2 + by2
+ cx + dy + e = 0, students can
use the method for completing the square to put the equation into
standard
form and can recognize whether the graph of the equation is a circle ,
ellipse,
parabola, or hyperbola. Students can then graph the equation.
Does the origin lie inside, outside, or on the
geometric figure whose equation is
x2 + y2 - 10x + 10y - 1 = 0? Explain your
reasoning. (ICAS 1997)
|
|
| |
18.0 Students use fundamental counting principles to compute
combinations and
permutations .
|
|
| |
19.0 Students use combinations and permutations to compute
probabilities.
|
|
| |
20.0 Students know the binomial theorem and use it to expand binomial
expressions
that are raised to positive integer powers.
|
|
| |
21.0 Students apply the method of mathematical induction to prove
general statements
about the positive integers.
|
|
| |
22.0 Students find the general term and the sums of arithmetic series
and of both
finite and infinite geometric series.
|
|
| |
23.0 Students derive the summation formulas for arithmetic series and
for both
finite and infinite geometric series.
|
|
| |
24.0 Students solve problems involving functional concepts, such as
composition,
defining the inverse function and performing arithmetic operations on
functions.
Which of the following functions are their own inverse functions? Use
at least
two different methods to answer this question and explain your methods:
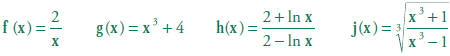
(ICAS 1997)
|
|
| |
25.0 Students use properties from number systems to justify steps in
combining
and simplifying functions.
|
|
Start solving your Algebra Problems
in next 5 minutes!
 |
 |
 |
|
Algebra Helper
Download (and optional CD)
Only $39.99
|
|
Click to Buy Now:
OR
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
2Checkout.com is an authorized reseller
of goods provided by Sofmath
|
|
Attention: We are
currently running a special promotional offer
for Algebra-Answer.com visitors -- if you order
Algebra Helper by midnight of
December 26th
you will pay only $39.99
instead of our regular price of $74.99 -- this is $35 in
savings ! In order to take advantage of this
offer, you need to order by clicking on one of
the buttons on the left, not through our regular
order page.
If you order now you will also receive 30 minute live session from tutor.com for a 1$!
|
You Will Learn Algebra Better - Guaranteed!
Just take a look how incredibly simple Algebra Helper is:
Step 1
: Enter your homework problem in an easy WYSIWYG (What you see is what you get) algebra editor:
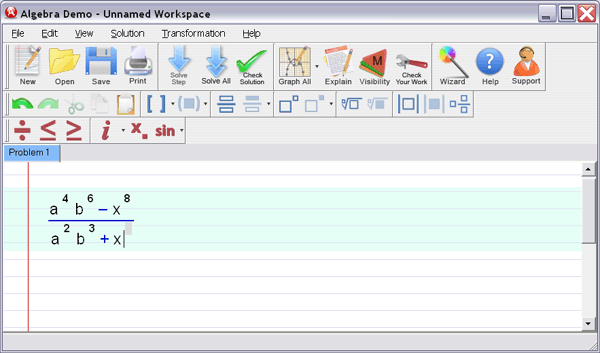
Step 2 :
Let Algebra Helper solve it:
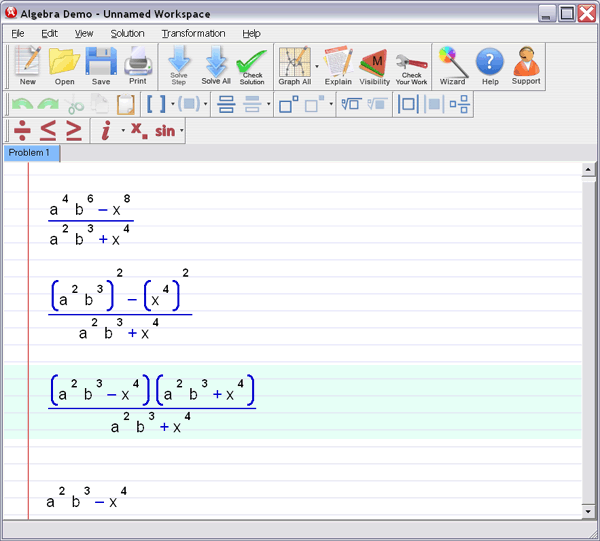
Step 3 : Ask for an explanation for the steps you don't understand:
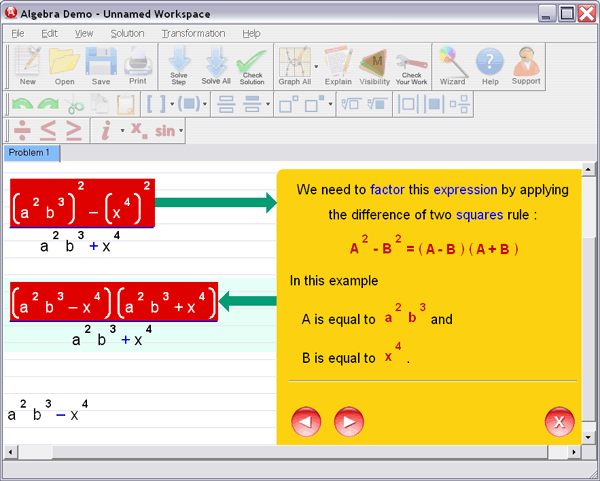
Algebra Helper can solve problems in all the following areas:
- simplification of algebraic expressions (operations
with polynomials (simplifying, degree, synthetic division...), exponential expressions, fractions and roots
(radicals), absolute values)
- factoring and expanding expressions
- finding LCM and GCF
-
(simplifying, rationalizing complex denominators...)
- solving linear, quadratic and many other equations
and inequalities
(including basic logarithmic and exponential equations)
- solving a system of two and three linear equations
(including Cramer's rule)
- graphing curves (lines, parabolas, hyperbolas, circles,
ellipses, equation and inequality solutions)
- graphing general functions
- operations with functions (composition, inverse, range, domain...)
- simplifying logarithms
- basic geometry and trigonometry
(similarity, calculating trig functions, right triangle...)
- arithmetic and other pre-algebra topics
(ratios, proportions, measurements...)
ORDER NOW!
 |
 |
 |
|
Algebra Helper
Download (and optional CD)
Only $39.99
|
|
Click to Buy Now:
OR
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
2Checkout.com is an authorized reseller
of goods provided by Sofmath
|
|
|
 |
| |
| "It
really helped me with my homework. I was
stuck on some problems and your software walked me
step by step through the process..." |
| C. Sievert, KY
| |
| |
 |
| |
Sofmath
19179 Blanco #105-234
San Antonio, TX 78258
|
Phone:
(512) 788-5675
Fax: (512) 519-1805
| | |