For the Math A Examination :
The basic constructions required for the Math A
Examination include:
* copy a line segment
* bisect a line segment
* copy an angle
* bisect an angle
* construct a perpendicular line through a point not on a line
• construct a perpendicular line through a point on a line
• construct a line parallel to the given line
In the space below, show all valid constructions on the following:
1. Copy a line segment .
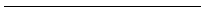
2. Bisect a line segment.

3. Copy an angle.
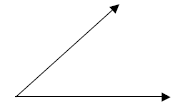
4. Bisect an angle.
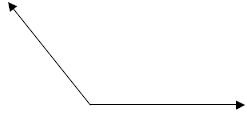
5. Construct a perpendicular line
through a point not on a line.
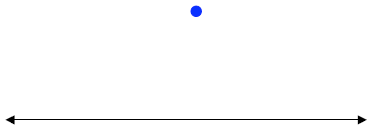
6. Construct a perpendicular line
through a point on a line.

7. Construct a line parallel
to the given line.
Create an Equilateral Triangle
1. Given line BC, create an equilateral triangle, with Line BC as the
base.
2. Create an arc the same length as line BC. The center of the arc is
at point B, and the start of the arc is at point C.
3. Create a second arc the same length as line BC. The center of the
arc is at point C, and the start of the arc is at point B. These two arcs
intersect at point A.
4. Create a line from point B to point A.
5. Create a line from point C to point A.
* Line BC, BA and CA form an equilateral triangle.
Construct the center point of a given circle
1. Begin with a circle, but no center point.
2. Draw chord AB.
3. Construct the perpendicular bisector of chord AB. Let C and D be
the points where it intersects the circle . (Refer to the construction of a
perpendicular bisector.)
4. Chord CD is a diameter of the circle . Construct point P, the
midpoint of diameter CD. Point P is the center point of the circle .
(Refer to the construction of a the midpoint of a line segment.)
Given a triangle, inscribe a circle
1. Begin with triangle KLM.
Construct the bisectors of < K and < L. (Refer to the angle bisector
construction.)
2. Let point Q be the intersection of the two angle bisectors.
Construct a line through point Q, perpendicular to line segment KL.
Let point R be the point of intersection. (Refer to the construction of
a perpendicular line through a given point.)
3. Center the compass on point Q, and draw a circle through point R.
The circle will be tangent to all three sides of a triangle.
MATH A 2002
25. Construct a triangle with sides of lengths a, b, and c, as
shown below. Be sure the longest side of your triangle lies
on PQ and that point P is one of the triangle’s vertices.
[Show all arcs necessary for a valid construction.]
a __________
b ______________
c __________________
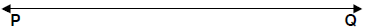
MATH A 2003
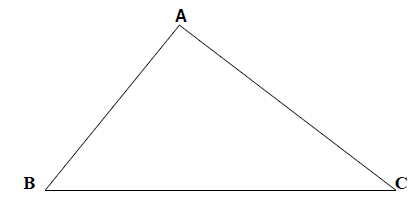
25. On the accompanying diagram of  ABC,
use a
ABC,
use a
compass and a straightedge to construct a median from A
to BC.