2008-2009 Mathematics Curriculum Guides
T
i
m
e |
Chapter |
MPS Learning Targets |
Wisconsin State Framework Assessment
Descriptors |
District Model
CABS |
District
Vocabulary |
J
a
n
u
a
r
y |
Chapter 6:
Geometry
•6.1 w/
Mini Lab
•6.2 w/
Mini Lab
•6.4 w/
Mini Lab
•6.5a
•6.7
•6.8
•6.9 w/
Mini Lab
|
Geometry:
Learning Target #2
Analyze relationships among figures
and their parts, including the
Pythagorean Theorem, using
properties of plane and coordinate
geometry, and use proportional
reasoning, transformations, and
spatial visualization in problem-solving
situations. (6.1, 6.2, 6.4,
6.5a, 6.7, 6.8, 6.9)
|
Mathematical Processes:
Mathematical Processes are embedded throughout all lessons when,
for example, students are asked to provide written justifications and
explanations, pose problems, and represent concepts
Geometry:
C.a.1 Identify, describe and analyze properties of figures,
relationships among figures and relationships among their parts (e.g.,
parallel, perpendicular and congruent sides, various types of angles
and triangles, complementary and supplementary angles, sum of
angles in a triangle). (6.1, 6.2, 6.4, 6.5a)
C.b.5 Use transformations and symmetry to solve problems. (6.7,
6.8, 6.9)
C.b.7 Use the two-dimensional rectangular coordinate system to
describe and characterize properties of geometric figures. Identify
and apply symmetry about an axis. (6.7, 6.8, 6.9) |
We hope these
district CABS will
be used to continue
and expand the
formative
assessment (i.e.
assessment for
learning vs.
assessment of
learning) initiatives
promoted by the
MMP.
Geometry:
“Analyze
Properties”
“Parallelogram
WXYZ”
“Understanding
Rectangles”
“Describing
Figures”
“Parallel/Perpendicu
lar”
“Complementary
and Supplementary
Angles”
“Reflecting”
|
•Angles
•Parallel
•Perpendi-cular
•Triangles
•Symmetry
•Axis of
symmetry
•Transfor-mations
|
| |
|
|
|
J
a
n
u
a
r
y
/
F
e
b
r
u
a
r
y |
Chapter 7:
Geometry:
Measuring
Area and
Volume
Essential:
•7.1 w/ Mini
Lab
•7.2 (skip
lab)
•7.3 (use
resource
pages
only)
•7.4a
•7.4
•7.5 w/
Mini Lab
•7.6 w/
Mini Lab
•7.7a
•7.7 |
Measurement:
Learning Target #3
Select and use appropriate tools and
procedures to solve problems
requiring direct measurements and
indirect measurements (e.g.,
perimeter, area, surface area, volume,
angles, and segments). (7.1, 7.2, 7.3,
7.5, 7.6, 7.7, 7.8, 7.9)
Geometry:
Learning Target #2
Analyze relationships among figures
and their parts, including the
Pythagorean Theorem, using
properties of plane and coordinate
geometry, and use proportional
reasoning, transformations, and
spatial visualization in problemsolving
situations. (7.4,7.7a, 7.7,
7.8)
|
Mathematical Processes:
Mathematical Processes are embedded throughout all lessons when,
for example, students are asked to provide written justifications and
explanations, pose problems, and represent concepts.
Measurement
D.c.3 Determine the perimeter/area of two-dimensional figures.
(7.1, 7.2, 7.3)
D.c.4 Determine the surface area/ volume of three-dimensional
figures. (7.5, 7.6, 7.7, 7.8)
Geometry
C.b.6 Visualize 3-dimensional figures in problem-solving situations.
(7.4a, 7.4, 7.7a, 7.7, 7.8)
|
We hope these district
CABS will be used to
continue and expand
the formative
assessment (i.e.
assessment for
learning vs.
assessment of
learning) initiatives
promoted by the
MMP.
Measurement:
“2-D Cross”
“Rectangular Lot”
“Dimension
Dilemma”
“Suzanne’s Logic”
“Stacking Blocks”
“Oatmeal Container”
“3-D Tower”
“Non-Shaded
Portions
Geometry:
“Paper Tube”
“Sadie’s Perspective”
“Making
Conjectures”
“Scott’s Reasoning” |
•Surface
area |
| |
| |
|
|
|
F
e
b
r
u
a
r
y |
Chapter 8:
Probability
Essential:
•8.1
•8.2a (#1-5
only)-
combine
w/
•8.2 or
Mathscape:
Looking
behind the
Numbers,
pages. 28-29
•8.3 w/ Mini
Lab or
Mathscape:
Looking
behind the
Numbers,
pages. 30-31
•8.4 w/
Mini Lab
•8.5
•8.6 w/
Mini Lab
•8.7 |
Statistics and Probability:
Learning Target #5
Design and analyze experiments
with simple and complex events,
predict likelihood of outcomes , and
justify strategies based on
theoretical and experimental
probabilities. (8.1, 8.2a, 8.2, 8.3,
8.4, 8.5, 8.6, 8.7)
|
Mathematical Processes:
Mathematical Processes are embedded throughout all lessons when,
for example, students are asked to provide written justifications and
explanations, pose problems, and represent concepts.
Statistics and Probability
E.a.3 Analyze, evaluate, and critique methods and conclusions of
statistical experiments (e.g., randomness, sampling techniques,
surveys). (8.7)
E.b.4 Emphasize on likelihood of occurrence of simple and complex
events using experimental and theoretical probability. The complete
10th grade descriptor is: Determine the likelihood of occurrence of
simple and complex events (e.g., combinations and permutations,
fundamental counting principle, experimental versus theoretical
probability and independent, dependent and conditional probability).
(8.1, 8.2a, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6) |
CABS will be used to
continue and expand
the formative
assessment (i.e.
assessment for
learning vs.
assessment of
learning) initiatives
promoted by the
MMP.
Statistics and
Probability:
“Representative?”
“Chip Pairs”
“Probability Candy”
“Math Girls”
|
•Randomness
•Permutations
•Combinations
•Independent event
•Dependent
event
•Experiment
al probability
•Theoretical
probability
•Sample
Population |
| |
|
|
|
M
a
r
c
h |
Chapter 9:
Statistics and Matrices
Essentials:
•9.1
•9.2 OR
Mathscape:
Looking
behind the
Numbers,
pages. 6-7
•9.3 OR
Mathscape:
Looking
behind the
Numbers,
pages. 8,9,10
•9.4
•Combine
9.5 & 9.6
•9.7 |
Statistics and Probability:
Learning Target #4
Design and conduct investigations,
display data using appropriate
representations, analyze and
summarize data using measures of
central tendency and variation, and
evaluate methods and conclusions .
(9.1, 9.2, 9.3, 9.4, 9.5, 9.6, 9.7)
|
Mathematical Processes:
Mathematical Processes are embedded throughout all lessons when,
for example, students are asked to provide written justifications and
explanations, pose problems, and represent concepts.
Statistics and Probability
E.a.1 Organize, display, compare, and interpret data in a variety
of
ways in mathematical and real -world contexts (e.g. histograms, line
graphs, stem and leaf plots, scatter plots, box-and-whiskers, bar
charts, Venn diagrams, tables, circle graphs ). Grade 9 emphasize
organize, display, compare and interpret data in a variety of ways in
mathematical and real-world contexts e.g. histograms, stem-and-leaf
plots, scatter plots, boxplots, and tables. (9.1, 9.2, 9.3, 9.6, 9.7)
E.a.2 Emphasize organize, display, compare and interpret data in
a
variety of ways in mathematical and real-world contexts e.g.
histograms, stem-and-leaf plots, scatter plots, boxplots, and tables.
The complete 10th grade descriptor is: Interpret, analyze, and make
predictions from organized and displayed data (e.g., measures of
central tendency, such as mean, median, mode, and, measures of
variation such as standard deviation, mean, median, mode, range,
dispersion, outliers, line of best fit, percentiles). (9.4, 9.5)
|
CABS will be used to
continue and expand
the formative
assessment (i.e.
assessment for
learning vs.
assessment of
learning) initiatives
promoted by the
MMP.
Statistics and
Probability:
“Reading Survey”
“New Show Survey”
“Cuddly Critters”
“Pat’s Pie Chart ”
“School Supplies”
“Mary’s Mean”
“Box Plot”
“Histogram”
|
Histogram
•Mean
•Median
•Mode
•Box-and-
whiskers
plot
•Dimension |
| |
|
A
p
r
i
l |
Chapter 10:
Algebra: More
Equations
Essential:
•10.1a
•10.1 w/
Mini Lab
•10.2
•10.3
•10.4a w/ 10.4
•10.5
•Combine
10.6 & 10.7 |
Algebraic Relationships:
Learning Target #6
Analyze, describe, and generalize
mathematical and real-world
patterns of change and functional
relationships with emphasis on the
role of variable quantities . (10.3)
Algebraic Relationships:
Learning Target #7
Model, justify, and solve linear
equations and relationships using
translations among tables,
graphs/grids, and symbolic forms .
(10.1a, 10.2, 10.3, 10.4a, 10.4, 10.5,
10.6, 10.7)
Algebraic Relationships:
Learning Target #8
Explain use of properties (e.g.,
commutative, associative,
distributive) to evaluate expressions
and solve linear equations. (10.1,
10.4a, 10.4, 10.7) |
Mathematical Processes:
Mathematical Processes are embedded throughout all lessons when,
for example, students are asked to provide written justifications and
explanations, pose problems, and represent concepts.
Algebraic Relationships:
F.b.3 Emphasize solve linear equations. The complete 10th grade
descriptor is: Solve linear and quadratic equations , linear
inequalities and systems of linear equations and inequalities.
(10.1a,
10.2, 10.4a, 10.4, 10.5, 10.6, 10.7)
F.b.5 Translate between different representations and describe
the
relationship among variable quantities in a problem (e.g., tables,
graphs, functional notations, formulas ). (10.3)
F.c.6 Emphasize demonstrate understanding of the Distributive,
Commutative, and Associative properties by evaluating and
simplifying expressions. The complete 10th grade descriptor is:
Demonstrate understanding of properties by evaluating and
simplifying expressions. (10.1)
F.c.7 Demonstrate understanding of properties by solving linear
equations. The complete 10th grade descriptor is: Demonstrate
understanding of properties by solving linear and quadratic
equations, linear inequalities, and systems of linear equations and
inequalities with one or two variables. (10.5, 10.6, 10,7) |
CABS will be used to
continue and expand
the formative
assessment (i.e.
assessment for
learning vs.
assessment of
learning) initiatives
promoted by the
MMP.
Algebraic
Relationships:
“Sam’s Idea
|
•Inequality |
| |
| |
|
A
p
r
i
l
?
M
a
y |
Chapter 11:
Algebra:
Linear
Functions
Essential:
•11.1 w/ Mini
Lab
•11.2 OR
Mathscape:
Family
Portraits, page.
272
•11.3a
•11.3
•11.4 and
Mathscape:
Family
Portraits,
pages.
280-281
•11.5 and
Mathscape:
Family
Portraits,
pages.
282,283,
284, &
285
•11.6 w/
Mini Lab
•11.7 |
Algebraic Relationships:
Learning Target #6
Analyze, describe, and
generalize mathematical and
real-world patterns of
change and functional
relationships with emphasis
on the role of variable
quantities. (11.1, 11.2,
11.3a, 11.3, 11.4, 11.5,
11.7)
Algebraic Relationships:
Learning Target #7
Model, justify, and solve
linear equations and
relationships using
translations among tables,
graphs/grids, and symbolic
forms. (11.3, 11.5, 11.7)
Statistics and Probability:
Learning Target #4
Design and conduct
investigations, display data
using appropriate
representations, analyze and
summarize data using
measures of central
tendency and variation, and
evaluate methods and
conclusions. (11.6)
|
Mathematical Processes:
Mathematical Processes are embedded throughout all lessons when, for
example, students are asked to provide written justifications and
explanations,
pose problems, and represent concepts.
Algebraic Relationships:
F.a.1 Describe, recognize, interpret and translate graphical
representations of
mathematical and real-world phenomena on coordinate grids (e.g., slope,
intercepts, rate of change, linear and non-linear functions, and
quadratic,
exponential and constant functions). (11.3, 11.4, 11.5)
F.a.2 Analyze, generalize, and represent patterns of change
(e.g., direct and
inverse variations, including numerical sequences , patterns to a given
term,
algebraic expressions and equations ). (11.1, 11.2)
F.b.5 Translate between different representations and describe
the relationship
among variable quantities in a problem (e.g., tables, graphs, functional
notations, formulas). (11.3a, 11.3, 11.5, 11.7)
F.c.7 Demonstrate understanding of properties by solving linear
equations.
The complete 10th grade descriptor is: Demonstrate understanding of
properties by solving linear and quadratic equations, linear
inequalities, and
systems of linear equations and inequalities with one or two variables.
(11.5,11.7)
Statistics and Probability
E.a.1 Organize, display, compare, and interpret data in a variety
of ways in
mathematical and real-world contexts (e.g. histograms, line graphs, stem
and
leaf plots, scatter plots, box-and-whiskers, bar charts, Venn diagrams,
tables,
circle graphs). Grade 9 emphasize organize, display, compare and
interpret
data in a variety of ways in mathematical and real-world contexts e.g.
histograms, stem-and-leaf plots, scatter plots, boxplots, and tables.
(11.6)
E.a.2 Emphasize organize, display, compare and interpret data in
a variety of
ways in mathematical and real-world contexts e.g. histograms,
stem-and-leaf
plots, scatter plots, boxplots, and tables. The complete 10th grade
descriptor is:
Interpret, analyze, and make predictions from organized and displayed
data
(e.g., measures of variation such as standard deviation, mean, median,
mode,
range, dispersion, outliers, line of best fit, percentiles). (11.6) |
We hope these
district CABS will
be used to continue
and expand the
formative
assessment (i.e.
assessment for
learning vs.
assessment of
learning) initiatives
promoted by the
MMP.
Algebraic
Relationships:
“ Similarities and
Differences ”
“All About the
Line”(omit x-
intercept)
“Equations and
Table”
“Create Your Own”
“Triangle Pattern”
“ Number Pattern ”
Statistics and
Probability:
“Scatter Plot”
|
•Functions
•Intercepts
•Scatter plot
•Line of best
fit
• Substitution |
| |
| |
|
|
M
a
y
/
J
u
n
e |
Chapter 12:
Algebra:
Nonlinear
Functions
and
Polynomials
Essential:
•12.1 |
Algebraic Relationships:
Learning Target #6
Analyze, describe, and generalize
mathematical and real-world
patterns of change and functional
relationships with emphasis on the
role of variable quantities. (12.1,
12.2, 12.3)
Algebraic Relationships:
Learning Target #8
Explain use of properties (e.g.,
commutative, associative,
distributive) to evaluate expressions
and solve linear equations. (12.3,
12.4, 12.5, 12.6, 12.7)
|
Mathematical Processes:
Mathematical Processes are embedded throughout all lessons when,
for example, students are asked to provide written justifications and
explanations, pose problems, and represent concepts.
Algebraic Relationships
F.a.1 Describe, recognize, interpret and translate graphical
representations of mathematical and real-world phenomena on
coordinate grids (e.g., slope, intercepts, rate of change, linear and
non-linear functions, and quadratic, exponential and constant
functions). (12.1)
F.b.4 Model and solve a variety of mathematical and real-world
problems by using algebraic expressions, equations and inequalities
(e.g., linear, exponential, quadratic). (12.2)
F.c.6 Emphasize demonstrate understanding of the Distributive,
Commutative, and Associative properties by evaluating and
simplifying expressions. The complete 10th grade descriptor is:
Demonstrate understanding of properties by evaluating and
simplifying expression. (12.3, 12.4, 12.5, 12.6, 12.7) |
We hope these district
CABS will be used to
continue and expand
the formative
assessment (i.e.
assessment for
learning vs.
assessment of
learning) initiatives
promoted by the
MMP.
Algebraic
Relationships:
“Bacterial Growth”
|
|
| |
Start solving your Algebra Problems
in next 5 minutes!
 |
 |
 |
|
Algebra Helper
Download (and optional CD)
Only $39.99
|
|
Click to Buy Now:
OR
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
2Checkout.com is an authorized reseller
of goods provided by Sofmath
|
|
Attention: We are
currently running a special promotional offer
for Algebra-Answer.com visitors -- if you order
Algebra Helper by midnight of
January 22nd
you will pay only $39.99
instead of our regular price of $74.99 -- this is $35 in
savings ! In order to take advantage of this
offer, you need to order by clicking on one of
the buttons on the left, not through our regular
order page.
If you order now you will also receive 30 minute live session from tutor.com for a 1$!
|
You Will Learn Algebra Better - Guaranteed!
Just take a look how incredibly simple Algebra Helper is:
Step 1
: Enter your homework problem in an easy WYSIWYG (What you see is what you get) algebra editor:
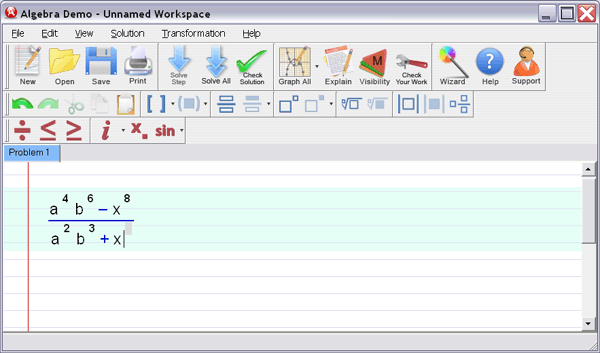
Step 2 :
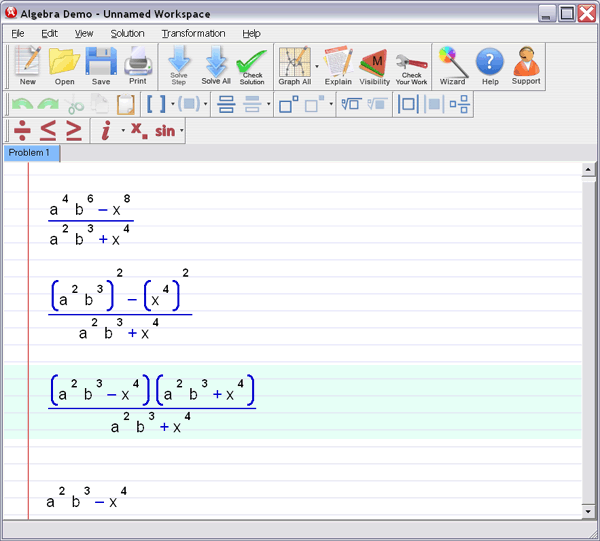
Let Algebra Helper solve it:
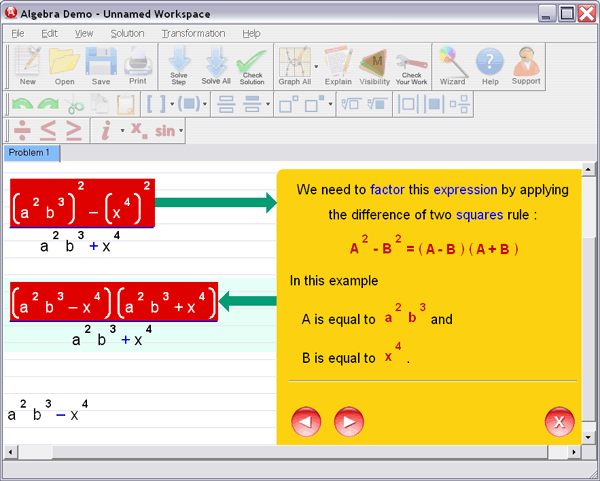
Step 3 : Ask for an explanation for the steps you don't understand:
Algebra Helper can solve problems in all the following areas:
- simplification of algebraic expressions (operations
with polynomials (simplifying, degree, synthetic division...), exponential expressions, fractions and roots
(radicals), absolute values)
- factoring and expanding expressions
- finding LCM and GCF
-
(simplifying, rationalizing complex denominators...)
- solving linear, quadratic and many other equations
and inequalities
(including basic logarithmic and exponential equations)
- solving a system of two and three linear equations
(including Cramer's rule)
- graphing curves (lines, parabolas, hyperbolas, circles,
ellipses, equation and inequality solutions)
- graphing general functions
- operations with functions (composition, inverse, range, domain...)
- simplifying logarithms
- basic geometry and trigonometry
(similarity, calculating trig functions, right triangle...)
- arithmetic and other pre-algebra topics
(ratios, proportions, measurements...)
ORDER NOW!
 |
 |
 |
|
Algebra Helper
Download (and optional CD)
Only $39.99
|
|
Click to Buy Now:
OR
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
2Checkout.com is an authorized reseller
of goods provided by Sofmath
|
|
|
 |
| |
| "It
really helped me with my homework. I was
stuck on some problems and your software walked me
step by step through the process..." |
| C. Sievert, KY
| |
| |
 |
| |
Sofmath
19179 Blanco #105-234
San Antonio, TX 78258
|
Phone:
(512) 788-5675
Fax: (512) 519-1805
| | |