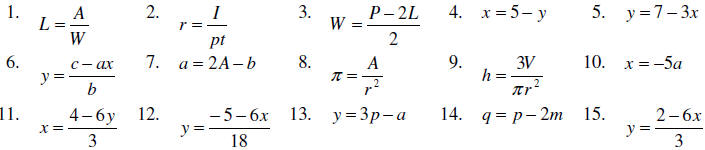A Literal Equation is an equation containing more than one
variable. We can solve a literal
equation for any one variable in terms of the others. For example, if we wish to
solve x − y = b
for x , we will need to add y to each side of the equation in order to isolate x
:
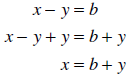
Example: Solve AC = V for A . Divide both sides of the
equation by C in order to isolate A:
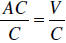 Cancel the C’s on the
left side of the equal sign .
Cancel the C’s on the
left side of the equal sign .
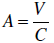
Example: Solve 2x + y = 5 for y :
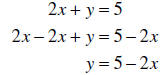
Example: Solve 2x + 3y = 6for y :
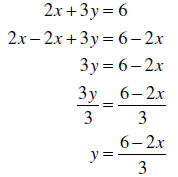
Note: This answer could also be written as
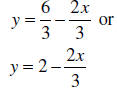
Example: Solve
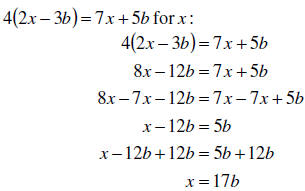
Example: Solve the following equation for y:
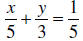 Multiply every term by
the LCD, 15.
Multiply every term by
the LCD, 15.
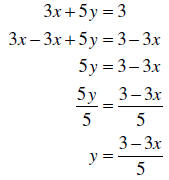
Example: Solve the following equation for h :
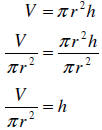
Exercises: Solve the following equations for the indicated
variable .
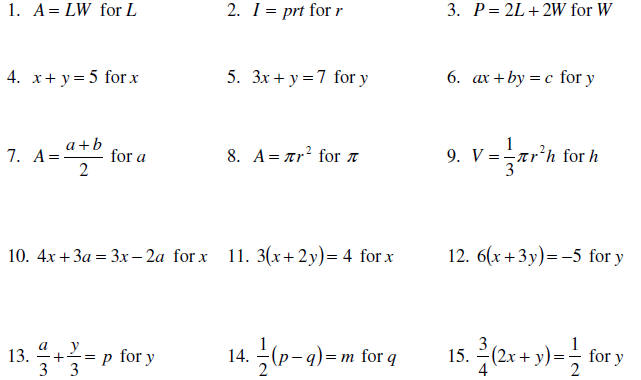
Answers: