Mathematics Content Expectations
Project Contents:
*Introductory Comments and Recommendations
*Math Overview of Content Expectations Taught in LCC Courses
*Individual Course Syllabus/Resources Aligned to Mathematics Expectations
*Alignment of ACCUPLACER Tests to High School Expectations
The process used for this alignment project was as
follows:
• The state expectations were studied, converted to a Microsoft Word document,
and copied into a table format to be used for
the alignment form.
• Expectations were aligned with each individual course syllabus. When a
matching syllabus item was not clear, the textbooks
used in the courses were checked to identify alignment.
• An expectation was marked as aligned if it was probable and foreseeable that a
significant portion of the expectation was met.
• The completed data was given to the department chair for review and input.
• The ACCUPLACER manual was reviewed, math tests completed and items aligned
with high school expectations.
Recommendation: I would recommend that this document be a “working document” –-
that instructors use it throughout the term
while teaching the course – and collaboratively it be edited, updated, expanded ,
and used as a starting point to assist LCC staff and
students in the alignment process of the K-16 educational program desired by the
state of Michigan.
| Form A: Math Alignment Table |
| Alignment to Math High School
Content Expectations |
| Math High School Content Expectations |
Prealgebra
Math 050 to
Summer 2006 |
Prealgebra
Math 050 to
Fall 2006 |
Introductory
Algebra
Math 107
Summer and
Fall 2006 |
Math 112 |
ACCUPLACER
Tests |
| ACCUPLACER TESTS: Arithmetic =
ARIT.pro; Elementary Algebra = ELAGLG.pro; College Level Math = CLM.pro |
| STRAND 1: QUANTITATIVE LITERACY
AND LOGIC (L) |
|
|
“In an increasingly complex world ,
adults are challenged to apply sophisticated quantitative knowledge and
reasoning in their professional and
personal lives. The technological demands of the workplace, the
abundance of data in the political and public policy context, and the
array of
information involved in making personal and family decisions of all
types necessitate an unprecedented facility not only with fundamental
mathematical, statistical, and computing ideas and processes, but with
higher- order abilities to apply and integrate those ideas and processes
in a
range of areas.”
The Michigan Grade Level Content Expectations in Mathematics for grades
K-8 prescribe a thorough treatment of number, including strong emphasis
on computational fluency and understanding of number concepts, to be
completed largely by the sixth grade. The expectations in this
Quantitative
Literacy and Logic strand provide a definition of secondary school
quantitative literacy for all students and emphasize the importance of
logic as part
of mathematics and in everyday life. They assume fluency (that is,
efficiency and accuracy) in calculation with the basic number operations
involving
rational numbers in all forms (including percentages and decimals),
without calculators.
Mathematical reasoning and logic are at the heart of the study of
mathematics. As students progress through elementary and middle school,
they
increasingly are asked to explain and justify the thinking underlying
their work. In high school, students peel away the contexts and study
the
language and thought patterns of formal mathematical reasoning. By
learning logic and by constructing arguments and proofs, students will
strengthen not only their knowledge and facility with mathematics, but
also their ways of thinking in other areas of study and in their daily
lives.
Connections and applications of number ideas and logic to other areas of
mathematics, such as algebra, geometry, and statistics, are emphasized
in
this strand. Number representations and properties extend from the
rational numbers into the real and complex numbers, as well as to other
systems
that students will encounter both in the workplace and in more advanced
mathematics. The expectations for calculation, algorithms and estimation
reflect important uses of number in a range of real-life situations.
Ideas about measurement and precision tie closely to geometry.
1 Estry, D., & Ferrini-Mundy, J. (January, 2005). Quantitative Literacy
Task Force Final Report and Recommendations. East Lansing: Michigan
State University. |
STANDARD L1: REASONING ABOUT NUMBERS,
SYSTEMS, AND QUANTITATIVE SITUATIONS
Based on their knowledge of the properties of arithmetic
students understand and reason about numbers, number
systems, and the relationships between them. They
represent quantitative relationships using mathematica
symbols, and interpret relationships from those
representations. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
ARIT.pro |
| L1.1 Number Systems and Number Sense |
|
|
|
|
|
L1.1.1 Know the different properties that hold in
different number systems, and recognize that the
applicable properties change in the transition from
the positive integers, to all integers, to the rational
numbers, and to the real numbers. |
 |
 |
|
|
ARIT.pro |
L1.1.2 Explain why the multiplicative inverse of
a
number has the same sign as the number, while the
additive inverse of a number has the opposite sign. |
 |
 |
 |
|
ARIT.pro
ELAGLG.pro |
L1.1.3 Explain how the properties of
associativity,
commutativity, and distributivity, as well as identity
and inverse elements, are used in arithmetic and
algebraic calculations . |
 |
 |
 |
|
ARIT.pro
ELAGLG.pro |
L1.1.4 Describe the reasons for the different
effects
of multiplication by, or exponentiation of, a positive
number by a number less than 0, a number between
0 and 1, and a number greater than 1. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
ARIT.pro
ELAGLG.pro
CLM.pro |
L1.1.5 Justify numerical relationships (e.g.,
show that
the sum of even integers is even; that every integer
can be written as 3m+k, where k is 0, 1, or 2, and m
is an integer; or that the sum of the first n positive
integers is n (n+1)/2). |
 |
 |
|
 |
|
L1.1.6 Explain the importance of the irrational
numbers and in basic right triangle trigonometry ; the
importance of π because of its role in circle
relationships; and the role of e in applications such
as continuously compounded interest . |
|
|
|
 |
CLM.pro |
| L1.2 Representations and Relationships |
|
|
|
|
|
L1.2.1 Use mathematical symbols (e.g., interval
notation, set notation, summation notation) to
represent quantitative relationships and situations. |
|
|
 |
 |
CLM.pro |
L1.2.2 Interpret representations that reflect
absolute
value relationships (e.g. l x - a l ≤ b, or a ± b) in such
contexts as error tolerance. |
|
|
 |
|
ELAGLG.pro |
L1.2.3 Use vectors to represent quantities that
have
magnitude and direction; interpret direction and
magnitude of a vector numerically, and calculate the
sum and difference of two vectors. |
|
|
|
|
|
L1.2.4 Organize and summarize a data set in a
table,
plot , chart, or spreadsheet; find patterns in a display
of data; understand and critique data displays in the
media |
 |
 |
 |
|
ARIT.pro
ELAGLG.pro |
| L1.3 Counting and Probabilistic Reasoning |
|
|
|
|
|
L1.3.1 Describe, explain, and apply various
counting
techniques (e.g., finding the number of different 4-
letter passwords; permutations; and combinations);
relate combinations to Pascal’s triangle; know when
to use each technique. |
|
|
|
|
|
to use each technique.
L1.3.2 Define and interpret commonly used
expressions of probability (e.g., chances of an event,
likelihood , odds). |
|
|
|
|
|
L1.3.3 Recognize and explain common probability
misconceptions such as “hot streaks” and “being
due.” |
|
|
|
|
|
Start solving your Algebra Problems
in next 5 minutes!
 |
 |
 |
|
Algebra Helper
Download (and optional CD)
Only $39.99
|
|
Click to Buy Now:
OR
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
2Checkout.com is an authorized reseller
of goods provided by Sofmath
|
|
Attention: We are
currently running a special promotional offer
for Algebra-Answer.com visitors -- if you order
Algebra Helper by midnight of
January 22nd
you will pay only $39.99
instead of our regular price of $74.99 -- this is $35 in
savings ! In order to take advantage of this
offer, you need to order by clicking on one of
the buttons on the left, not through our regular
order page.
If you order now you will also receive 30 minute live session from tutor.com for a 1$!
|
You Will Learn Algebra Better - Guaranteed!
Just take a look how incredibly simple Algebra Helper is:
Step 1
: Enter your homework problem in an easy WYSIWYG (What you see is what you get) algebra editor:
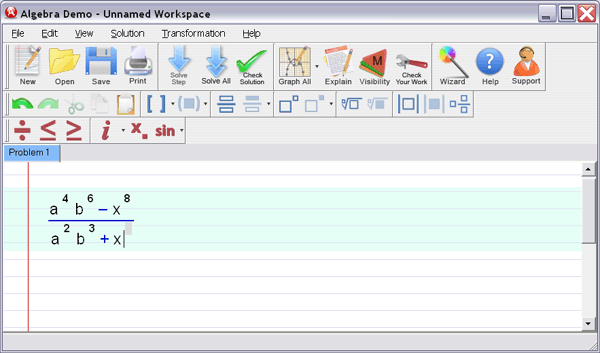
Step 2 :
Let Algebra Helper solve it:
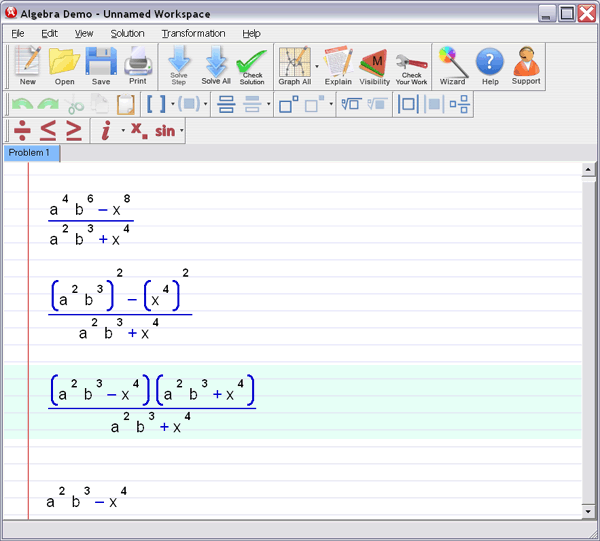
Step 3 : Ask for an explanation for the steps you don't understand:
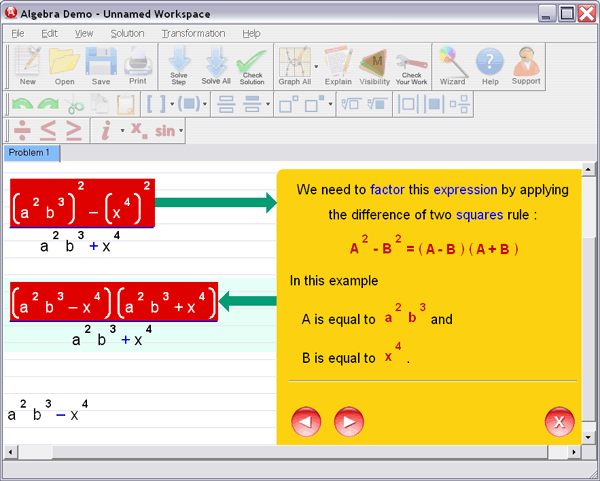
Algebra Helper can solve problems in all the following areas:
- simplification of algebraic expressions (operations
with polynomials (simplifying, degree, synthetic division...), exponential expressions, fractions and roots
(radicals), absolute values)
- factoring and expanding expressions
- finding LCM and GCF
-
(simplifying, rationalizing complex denominators...)
- solving linear, quadratic and many other equations
and inequalities
(including basic logarithmic and exponential equations)
- solving a system of two and three linear equations
(including Cramer's rule)
- graphing curves (lines, parabolas, hyperbolas, circles,
ellipses, equation and inequality solutions)
- graphing general functions
- operations with functions (composition, inverse, range, domain...)
- simplifying logarithms
- basic geometry and trigonometry
(similarity, calculating trig functions, right triangle...)
- arithmetic and other pre-algebra topics
(ratios, proportions, measurements...)
ORDER NOW!
 |
 |
 |
|
Algebra Helper
Download (and optional CD)
Only $39.99
|
|
Click to Buy Now:
OR
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
2Checkout.com is an authorized reseller
of goods provided by Sofmath
|
|
|
 |
| |
| "It
really helped me with my homework. I was
stuck on some problems and your software walked me
step by step through the process..." |
| C. Sievert, KY
| |
| |
 |
| |
Sofmath
19179 Blanco #105-234
San Antonio, TX 78258
|
Phone:
(512) 788-5675
Fax: (512) 519-1805
| | |