Idaho Department of Education
Content Standards |
Objective |
Sub Objectives |
Task Analysis |
Essential Vocabulary |
Sample Assessment |
| Standard 3: Concepts and Language
of Algebra and Functions |
Goal 3.1: Use algebraic symbolism as a
tool to represent mathematical
relationships. |
8.M.3.1.1 Use variables in
expressions , equations, and
inequalities.CL: D
Calc: CN
Content Limit: Evaluate an expression by substituting a
number for every variable in the expression. Items are
limited to at most three variables at a time. Items may
also check solutions to equations or inequalities by
substituting values for the variable (s) in an equation or
inequality. |
• Use variables in expressions,
equations, and
inequalities |
• apply order of operations to
variable expressions
• evaluate expressions by replacing variables with given
numbers |
• variable • algebraic expression •
evaluate • simplify |
• Evalute for n=3: 2n+5-n
• Evaluate the expression for m=5.2 and n=4.1:
5m-2n*3 |
|
|
|
|
8.M.3.1.2 Translate simple word statements and
story
problems into algebraic expressions and equations.
CL: D
Calc: CN
Content Limit: Items should be set in a real-world
context Expressions and equations may contain at
most
three operations and may require at most two grouping
symbols. May contain one or two variables. |
• Translate simple word statements and story
problems
into algebraic expressions and equations |
• assign variables to write algebraic expressions
• represent given mathematical vocabulary with
appropriate operational symbols |
• sum • difference • quotient • product •
less/greater •
than • increased/decreased by |
• An object's weight on Mars is 0.38 times the
object's
weight on Earth. Write an algebraic expression for an
object's weight on Mars. |
|
|
8.M.3.1.3 Use symbols “<,” “>,”“=,” “≠,” “≤,” and
“≥”
to express relationships.CL: D
Calc: CN
Content Limit: Items should be set in a real-world
context. Item may include integers between −50 and 50,
up to three operations, at most two grouping symbol,
and exponents limited to 2, 3, and 4. May include one
variable |
• Use symbols “<,” “>,”“=,” “≤,” “≥,” and “≠” to
express relationships |
• define symbols of inequality
• write inequalities and equations to represent numerical
relationships |
• not equal |
• Write the algebaric expression for:
y minus 4 is a negative number . |
Goal 3.2: Evaluate algebraic
expressions. |
8.M.3.2.1 Use and apply the following
properties in
evaluating algebraic expressions: commutative,
associative, identity, zero, inverse, distributive, and
substitution.CL: C
Calc: CN
Content Limit: Items can use positive fractions with no
more than two- digit numerators and denominators or
decimals less than ten-thousandths. Expressions may
include integers between −50 and 50, up to three
operations, at most two grouping symbol, and
exponents limited to 2, 3, and 4. May include one
variable. |
• Use and apply the following
properties in evaluating
algebraic expressions: commutative, associative,
identity, zero, inverse, distributive, and substitution |
• use associative and commutative
properties to
simplify expressions
• identify identity properties of addition and
multiplication
• identify inverse properties of addition and
multiplication
• apply distributive property to expressions
• describe zero property
• practice evaluating expressions using substitution |
• commutative • associative •
identity • zero • inverse •
distributive • substitution |
• Use the appropriate property to
simplify:
2.5+5.3+7.5
(n+14)(-8)
-2 x 13*5 |
|
|
|
|
8.M.3.2.2 Use the order of operations in
evaluating
simple algebraic expressions.CL: C
Calc: CN
Content Limit: Expressions may include parentheses,
exponents, multiplication, division, addition, and/or
subtraction. Items can use positive fractions with no
more than two-digit numerators and denominators or
decimals less than ten-thousandths. Roots are limited to
square roots and cube roots. Items require students to
compute only the cube root of 8, 27, 64, 125, or 1,000.
May include one or two variables. |
• Use the order of operations in evaluating
simple
algebraic expressions |
• recognize and apply correct order of operations |
|
• Evaluate:
n+(13-n)/5 for n=3 |
|
|
8.M.3.2.3 Simplify algebraic expressions.
CL: C
Calc: CN
Content Limit: Items can use positive fractions with no
more than two-digit numerators and denominators or
decimals less than ten-thousandths. Expressions may
include integers between −50 and 50, up to three
operations, at most two grouping symbol, and
exponents limited to 2, 3, and 4. May include one or
two variables. |
• Simplify algebraic expressions |
• apply propertyies from 8.M.3.2.1
• Illustrate simplifying expressions by combining like
terms and using distributive property |
• like terms |
• Simplify:
8c-3(c+5) |
|
Goal 3.3: Solve algebraic equations and inequalities. |
8.M.3.3.1 Solve one- and two-step
equations and
inequalities.CL: C
Calc: YES
Content Limit: Items can use positive fractions with no
more than one-digit numerators and denominators or
decimals less than ten-thousandths. Equations and
inequalities may include integers between −50 and 50.
Variable may appear on left or right side of equal or
inequality sign . |
• Solve one- and two-step equations
and inequalities |
• apply properties from 8.M.3.2.1
• apply addition and subtration properties of
equality/inequality
• apply multiplication and division properties of
equality/inequality including multiplicative
inverse/reciprocal |
• isolate • solution •
reciprocal/multiplicative inverse |
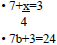 |
|
|
|
|
8.M.3.3.2 Match graphical representations with
simple
linear equations.CL: C, D
Calc: CN
Content Limit: The x- and y-axes may have different
scales. Linear equations will be given in slope-intercept 3
(y = mx + b) form. |
• Recognize linear equations in slope-intercept
form
• Match graphical representations with simple linear
equations |
• identify parts of a coordinate plane
• create a table of values given a linear equation and use
the ordered pairs to plot a line
• identify slope and y -intercept from y = mx + b and
represent as a graph |
• origin • x- and y-axes • ordered pair • slope •
y-intercept
• linear • slope intercept form • coordinate
plane |
• Which of the following is a graph of the
equation
y=2x-1?
• Graph 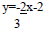 using 0,3 and 6 as the x
values using 0,3 and 6 as the x
values
by completing the table
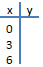 |
Goal 3.4: Understand the concept of
functions. |
8.M.3.4.1 Extend patterns and
identify a rule (function)
that generates the pattern using rational numbers.
CL: E
Calc: YES
Content Limit: Items may require a verbal description
of the pattern. Variables can be used to write the rule
(function). Items should not include more that two
variables or include more than two operations. Fraction
denominators limited to 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, and 10.
Decimals limited to tenths, hundredths, and
thousandths. Functions must be expressible as y = mx +b. Items may ask
the student to extend the pattern, state
the rule for the pattern, or both. |
• Extend patterns and identify a rule
(function) that
generates the pattern using rational numbers |
• recognize input/output
relationships of functions
• represent function using a table
• write a rule to extend pattern
• use function notation to represent relationship
(y =
mx+ b as f(x) = mx + b) |
• function • function rule •
input/output • relation |
|
|
|
|
|
8.M.3.4.2 Use relationships to explain how a
change in
one quantity may result in a change in another, and
identify the relationship as a positive, negative, or
neither.CL:
Calc:
Content Limit: Assessed in the classroom, not on the
ISAT. |
• Use relationships to explain how a change in
one
quantity may result in a change in another, and identify the
relationship as a positive, negative, or neither |
• use a graph or table to show how a change in
one
quantity affects the other quantity |
• quantity • rate of change |
|
|
|
8.M.3.4.3 Use appropriate vocabulary and
notations. CL:
Calc:
Content Limit: Assessed in the classroom, not on the
ISAT. |
• Use appropriate vocabulary and notations |
• communicate using correct mathematical
terminology |
|
|
Goal 3.5: Represent equations,
inequalities and functions in a variety
of formats. |
8.M.3.5.1 Represent a set of data in
a table, as a graph,
and as a mathematical relationship.CL: C, D
Calc: CN
Content Limit: On the graph, x- and y-axes may have
different scales . Items do not require students to graph
or generate a table of a non-linear relation; students
may read points off of a graph of a non-linear relation.
Items may include real-world context. Given a
continuous (i.e., individual points not indicated) linear
graph,
students will generate a table of values.
Relationship is presented as a table, graph, or equation.
The answer options will include a table, a graph, or an
equation. |
• Represent a set of data in a table
as a graph, and as an
equation |
• establish input/output relationship
between data in
table and graph or equation |
• data table |
|
| |
Goal 3.6: Apply functions to a variety
of problems. |
8.M.3.6.1 Use patterns and linear
functions to represent
and solve problems.CL: D
Calc: YES
Content Limit: Patterns may include rational numbers.
Linear functions are limited to whole number variable
values. |
• Use patterns and linear functions
to represent and
solve problems |
• identify patterns in problems
• discover function rule for pattern
• evaluate using function |
|
|
|
|