1. On page 5 in the text, backward stability is defined as
follows:
If alg(x) is our algorithm for f(x), including the effects of round-
off, we call alg(x) A backward stable algorithm for f(x) if for all x there
is A \small" δx such that alg(x) = f(x +δx). δx is called the backward
error. Informally, we say that we get the exact answer (f(x + δx))
for A slightly wrong problem (x +δx).
Identify the x and f(x) for
• systems of linear equations.
Solution : Ax = b, where A and b are the input, the x in the definition, and x =
A-1b
is the f(x), the output.
•
Least Squares problems .
Solution: This problem is
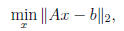
where A and b are the input, the x in the definition, and
the solution to the normal
equation
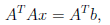
is the f(x), the output.
• QR factorization.
Solution: The QR factorization is
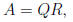
where Q is orthogonal and R is upper triangular. Here A is
the input, the x in the
definition, and Q and R are the output f(x).
In the first two cases , also identify a backward stable algorithm for computing
f(x). In
the third case, explain why a backward stable algorithm might NOT exist. We
exclude
overflow/underflow considerations.
Solution: GEPP is backward stable for solving linear systems of equations as
long as the
element growth factor is controled . QR factorization is a good method for
solving both linear
equations and least squares problems.
Computing a backward stable QR factorization would be very tricky. This is
because Q is
an orthogonal matrix. By definition, even the Q factor in the perturbed output
f(x + δx)
must still be exactly orthogonal. It is unlikely any algorithm will be able to
do so in general.
2. Let
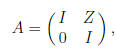
where 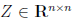 and I is the
identity matrix. Express the 2-norm condition number of A
and I is the
identity matrix. Express the 2-norm condition number of A
using the singular values of Z .
Solution: Let 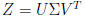 be the SVD of Z, then
be the SVD of Z, then
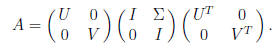
Of the three matrices on the right hand side, only the
middle matrix is not orthogonal, and
its singular values are the singular values of A. Each diagonal entry of induces
a pair
of singular values in the 2 × 2 matrix
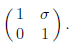
These singular values are
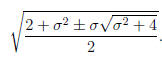
The singular values of A are all these pairs of singular
values. Hence the 2-norm condition
number of A is
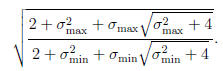
3. Let T be an m × m lower triangular matrix and b be an
m-vector. Show how to solve the
m × m linear system of equations Tx = b in about m^2 ops.
Solution: Forward substitution.
4. Let 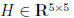 be a matrix of the form
be a matrix of the form
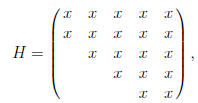
where all the x's denote non- zero entries . Matrices with
the non-zero pattern of H are called
Hessenberg matrices. Show how to use 4 Givens rotations to QR factorize H.
Solution: A Givens rotation is of the form
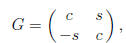
where c^2 + s^2 = 1. It is used to zero out a component in
a 2 dimensional vector. We apply
a Givens rotation to zero out the (2; 1) entry:
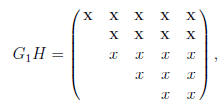
where the x entries represent entries that have been
changed .
There are 4 subdiagonal entries in H. We use 4 Givens rotations, executed one by
one, to
zero out all of them.
5. Consider the following variant of the least squares
problem:
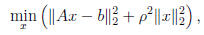
where the matrix A, the vector b and scalar ρ > 0 are given.
Find the normal equation for
this problem and develop a QR-type algorithm for solving the normal equation.
Solution: We let
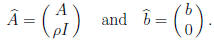
Then the given problem becomes
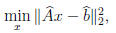
to which the standard QR factorization method can be
applied .