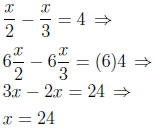The vast majority of the problems on the test come from
your assigned homework.
Section 1.1 covers the real number system . In this section we learned how to
classify subsets
of the real numbers . We learned how to represent sets of numbers by graphing on
a number
line, using set builder notation, inequalities , and interval notation. We also
learned the
definition of absolute value. Be familiar with the following definitions.
Definition (Natural Numbers).
The set of natural numbers are the numbers we use for counting:
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, . . .}
Definition (Whole Numbers).
The set of whole numbers include the natural numbers together with 0:
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, . . .}
Definition (Integers).
The set of integers include the natural numbers, 0, and the negatives of
the natural numbers:
{. . . ,−5,−4,−3,−2,−1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, . . .}
In each of the sets above, the three dots are called ellipsis. They
indicate that the pattern
of numbers continue forever.
Definition (Rational Numbers).
The set of rational numbers is the set of numbers that can be written as
fractions where
both the numerator and the denominator are integers.
{ x|x can be written in the form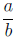 (b ≠ 0)
where a and b are integers.}
(b ≠ 0)
where a and b are integers.}
The set of rational numbers include the set of integers since an integer can be
written as a
fraction with 1 in the denominator .
Definition (Irrational Numbers).
Irrational numbers are number that are not rational. An irrational number
can not be
written as a ratio of two integers . The set of irrational numbers is
{x|x is a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal.}
Familiarize yourself with the box on page 10 of your text that shows the
relationship between
set notation, graphs, and interval notation.
The absolute value of a number is its distance from the origin. For
example, |3| = 3 since
the number 3 is 3 units from the origin. Likewise, | − 3| = 3 since the number
-3 is 3 units
from the origin.
Definition (Absolute Value).
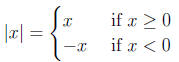
Section 1.2 covers the arithmetic properties of the real
numbers. Make sure you are familiar
with the following properties.
Suppose a, b, and c are real numbers:
(a + b) + c = a + (b + c)
is the associative property of addition.
(ab)c = a(bc)
is the associative property of multiplication.
a + b = b + a
is the commutative property of addition.
ab = ba
is the commutative property of multiplication.
a(b + c) = ab + bc
is the distributive property.
a + 0 = 0 + a = a
The number 0 is called the additive identity.
a · 1 = 1 · a = a
The number 1 is called the multiplicative identity .
Section covers natural number exponents. In this section we defined natural
number exponents
and developed several properties of exponents.
Definition (Natural Number Exponents).
If n is a natural number, then
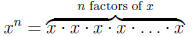
The real number x is called the base, and the natural number n is called the
exponent.
The product rule of exponents . If m and n are natural numbers, then
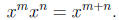
The power rule of exponents.
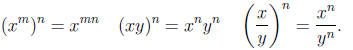
Zero exponents . If x ≠ 0, then x0 = 1.
Negative exponents. If x ≠ 0, then
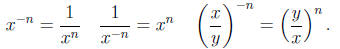
Quotient rule of exponents
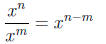
We use these properties to simplify exponential
expressions.
Example.
Simplify the following expression.
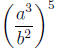
Solution .
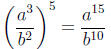
Example.
Simplify the following expression.
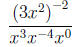
Solution.
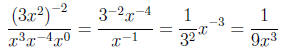
Example.
Simplify the following expression.
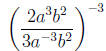
Solution.
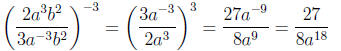
Section 1.4 covers scientific notation. A number is in
scientific notation if it is written in the
form
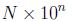
Where 1 ≤ |N| < 10.
Section 1.5 covers solving linear equations . An equation is linear if it can be
written in the
form ax + c = 0. An equation is linear if the exponent on the variable is 1.
Familiarize
yourself with the procedure for solving linear equations in the blue box on page
50 of your
book. Recall that like terms are terms with the same variables raised to the
same powers.
Example.
Solve the following equation.
3(x − 5) + 10 = 2(x + 4)
Solution.
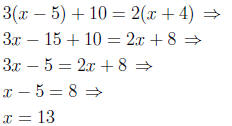
Example.
Solve the following equation.
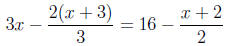
Solution.
The first step is to clear all fractions by multiplying each term in the
equation by the least
common denominator (LCD), then solve as usual.
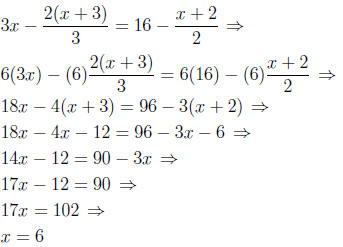
Example.
Solve the following equation.
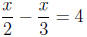
Solution.