Tue., Mar. 11:
Midterm Test (in class)
Thu., Mar. 6:
Bring review questions
Read: § 5.3 - 5.4
151: 3 - 5
And this: Conduct some experiments in cryptography using computers (PDF
for printing - classical HTML for terminal window browsing).
Tue., Mar. 4:
Written Assignment No. 2 (PDF for printing - classical HTML for terminal
window browsing) is due.
Thu., Feb. 28:
Read: § 5.1 - 5.2
151: 1, 2
And this: Write a Maple procedure that given a univariate polynomial f (x) and a
polynomial b(x) of degree at least 1 returns the vector of coefficients
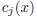 for the
for the
b-adic expansion of f(x)
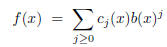
where 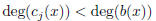 for each j ≥ 0.
for each j ≥ 0.
Tue., Feb. 26:
Announcement: The midterm test will be held on Tuesday, March 11.
Scan: Chapter 4
Exercises:
137: 1, 4
And this: Write a Maple procedure that given a base b ≥ 2 and a triple of
vectors
equivalent to the base b representation of a positive rational number - each
vector
consisting of digits relative to the base b, with the vectors in order being (a)
the digit
sequence (possibly empty) to the left of the decimal point , (b) the digit
sequence
(possibly empty) to the right of the decimal point before the repetition
pattern, and
(c) the digit sequence (if any) that repeats - returns the positive rational
number
as a fraction m/n where m and n are positive integers without common divisor .
Read: § 8.1 - 8.4
Exercises:
1. Study the formulas and do the exercise found in this web page (PDF for
printing
|classical HTML for terminal window browsing).
2. What rational number is represented in base 8 by the vector triple
(u, v, w) = ([2], [1], [1, 5, 4, 6, 6, 3, 3]) ?
Tue., Feb. 19:
No class; the University will be in recess.
Thu., Feb. 14:
Read: § 3.4 - 3.6
Exercises:
93: 6 - 10
And this: Write a Maple procedure that when given a finite continued fraction,
presented as the vector 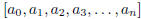 representing
representing
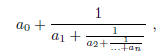
with the 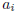 all integers
and
all integers
and 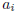 ≥ 1 for i ≥ 1, returns the rational
number it represents.
≥ 1 for i ≥ 1, returns the rational
number it represents.
Tue., Feb. 12:
Written Assignment No. 1 (PDF for printing |classical HTML for terminal
window browsing) is due.
Thu., Feb. 7:
Read: § 3.1 { 3.3
Exercises:
63: 12, 13
93: 1 - 5
And this: Examine all iterates of the Syracuse function applied to each integer
n up
to 10; 000 and find the integer n in that range having an iterate
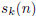 for which the
for which the
ratio 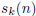 /n of the iterate to the starting
integer is largest. Hint: If the problem is
/n of the iterate to the starting
integer is largest. Hint: If the problem is
modified to consider only integers n up to 100, then the integer in that smaller
range
having an iterate with largest ratio is 27, and the iterate presenting the
largest ratio
is 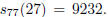
Tue., Feb. 5:
Read: xx 2.5 - 2.6
Exercises:
63: 6 - 11
And this: ssq will be the name for the function defined by
ssq(n; b) = 1 + ( sum of the squares of the base b digits
of n) :
In that code if the second variable b is not speci
ed, then it is understood
to be 10.
Conduct experiments with the base b having the values 2,
3, 5, and 6 to try to
determine what happens when ssq is iterated starting from various positive
integers
n.
Online slides (Firefox or IE+ MathPlayer or PDF ) for the
class are available.
Thu., Jan. 31:
Read: § 2.1 - 2.4
Exercises:
63: 1 - 5
And this: The Syracuse function s is defined for integers n by
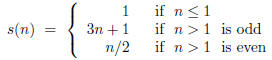
The iterates of s are
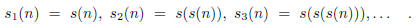
For example, 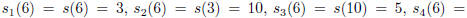
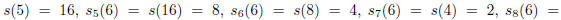
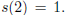 Since the 8th iterate of s applied to 6 is
1, all higher iterates of s applied
Since the 8th iterate of s applied to 6 is
1, all higher iterates of s applied
to 6 are 1.
Find the 5 smallest values of n for which the first 2n+1
iterations of s applied to n
fail to yield 1.
Post assignment: online slides (Firefox or IE+MathPlayer
or PDF) for the last exercise
are available.
Tue., Jan. 29: Acquire the textbook. Read through
chapter 1, and try some of what is
sketched there for yourself in Maple.
About free general purpose computer algebra systems : The
following items were
found through a web search, but none of them have been reviewed.
Axiom
Axiom has been in development since 1973 and was sold as a commercial product .
It
has been released as free software under the Modified BSD License. It is
sponsored
by CAISS, the Center for Algorithms and Interactive Scientific Software, at The
City
College of New York.
Maxima
Maxima is a descendant of Macsyma, the computer algebra system developed in the
late 1960s at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It is free under the
GNU
General Public License subject to some export restrictions from the U.S.
Department
of Energy. A proprietary version of Macsyma is also available.
SAGE
SAGE is something relatively new that is not a computer algebra system but
rather a
free unifying framework for various computer algebra systems, free and non-free,
such
as Maple, Mathematica, Axiom, Maxima, and a number of specialist systems. SAGE
can be operated , even across the network (though usually not without
permission),
in the window of a web browser.
Thu., Jan. 24:
First meeting: No assignment.
UP | TOP | Department